Stress and Its Impact on Your Health: How to Manage It Effectively

Introduction
Stress is an inevitable part of life. Whether it’s caused by work, relationships, financial pressures, or health concerns, everyone experiences stress at some point. While short-term stress can sometimes be beneficial—helping you stay alert and focused—chronic stress can have serious consequences on your physical and mental well-being.
In this article, we’ll explore how stress affects the body and mind, its impact on overall health, and effective strategies to manage it for a healthier and more balanced life.
What is Stress?
Stress is the body’s natural response to challenges or threats. When faced with a stressful situation, the body releases hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, triggering the “fight or flight” response. This reaction prepares the body to respond quickly to danger.
While this response is beneficial in emergencies, long-term exposure to stress can harm the body by keeping it in a constant state of alertness.
How Stress Affects Your Health
1. Physical Effects of Stress
Chronic stress can weaken the body’s ability to function properly, leading to various health issues:
A. Weakens the Immune System
- Stress hormones suppress immune function, making you more vulnerable to colds, flu, and infections.
- Increases inflammation, which contributes to autoimmune diseases and chronic illnesses.
B. Causes Heart Problems
- Long-term stress leads to high blood pressure, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Stress contributes to irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias) and cholesterol imbalances.
C. Disrupts Sleep Patterns
- Overthinking and anxiety can make it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep.
- Poor sleep quality worsens stress, creating a vicious cycle.
D. Triggers Digestive Issues
- Stress can cause stomachaches, acid reflux, and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
- Some people experience overeating or loss of appetite due to stress.
E. Leads to Muscle Pain and Tension
- Prolonged stress causes the body to remain tense, leading to headaches, neck pain, and back pain.
- Can worsen conditions like arthritis and fibromyalgia.
2. Mental and Emotional Effects of Stress
Stress doesn’t just affect the body—it also takes a toll on mental health:
A. Increases Anxiety and Depression
- Chronic stress raises cortisol levels, which can lead to persistent worry, panic attacks, and feelings of sadness.
- Over time, stress contributes to the development of depression and mood disorders.
B. Reduces Concentration and Memory
- Stress impairs cognitive function, making it harder to focus, learn, and recall information.
- Chronic stress has been linked to an increased risk of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease.
C. Causes Emotional Instability
- Stress can make people more irritable, impatient, or prone to angry outbursts.
- It affects relationships by causing miscommunication and emotional withdrawal.
D. Lowers Motivation and Productivity
- Stress reduces the brain’s ability to process information efficiently, leading to burnout, procrastination, and decreased work performance.
Effective Strategies for Managing Stress
While stress is unavoidable, you can take proactive steps to manage it and improve your well-being. Here are some science-backed techniques:
1. Practice Deep Breathing and Relaxation Techniques
- Deep breathing activates the parasympathetic nervous system, reducing stress hormones.
- Try 4-7-8 breathing: Inhale for 4 seconds, hold for 7 seconds, and exhale for 8 seconds.
- Meditation and mindfulness exercises help calm the mind and reduce anxiety.
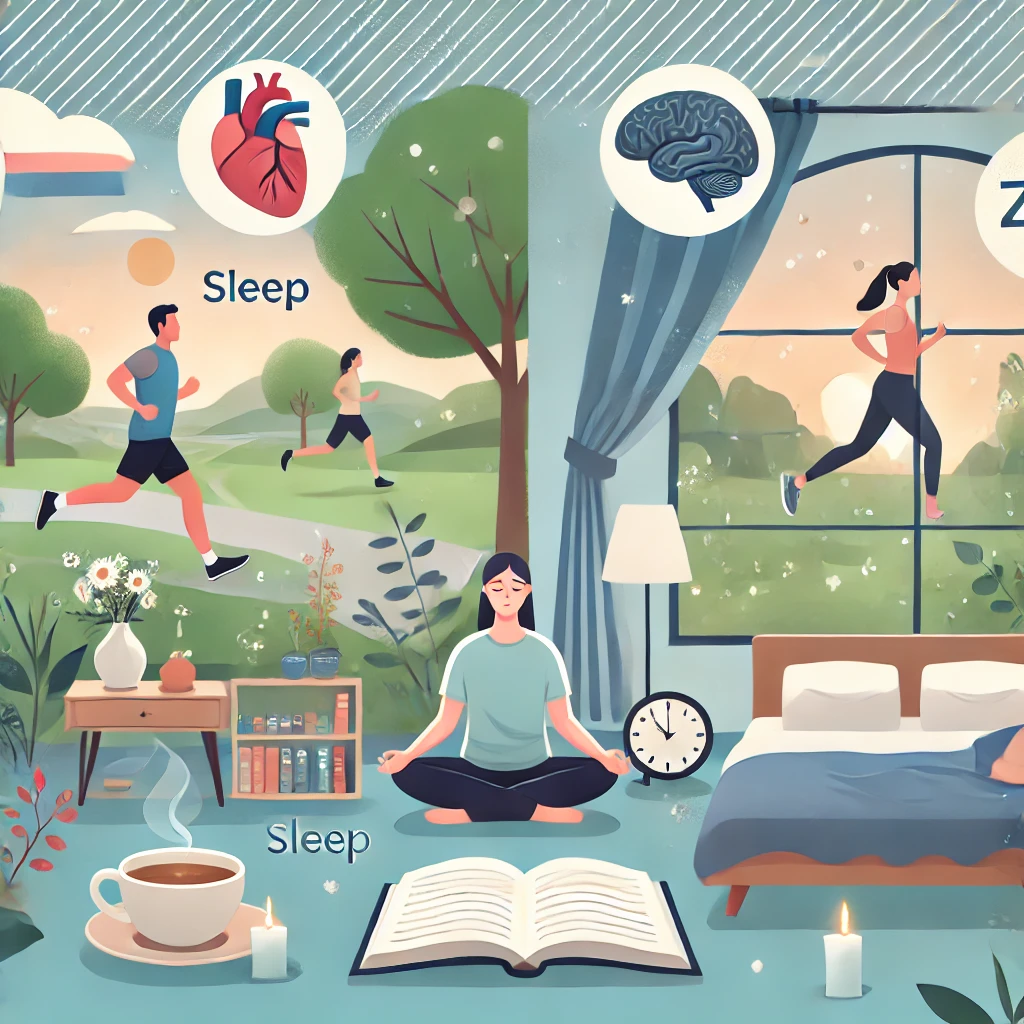
2. Exercise Regularly
- Physical activity reduces cortisol levels and releases endorphins, which are natural mood boosters.
- Activities like walking, yoga, dancing, or strength training improve stress resilience.
3. Get Quality Sleep
- Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night to allow the body to repair and rejuvenate.
- Avoid caffeine, screens, and heavy meals before bedtime.
4. Maintain a Balanced Diet
- Eat nutrient-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Avoid excessive sugar, caffeine, and processed foods, which can trigger stress.
5. Manage Your Time Wisely
- Break tasks into smaller steps to avoid feeling overwhelmed.
- Use planners, to-do lists, or digital apps to stay organized.
- Learn to say no to unnecessary commitments.
6. Connect with Loved Ones
- Talking to friends, family, or support groups can reduce stress and provide emotional relief.
- Social interactions boost oxytocin levels, reducing feelings of loneliness and anxiety.
7. Spend Time in Nature
- Studies show that spending time in green spaces, parks, or near water reduces stress and improves mood.
- A short 15-minute walk outside can have calming effects on the nervous system.
8. Engage in Hobbies and Activities You Enjoy
- Activities like painting, playing music, gardening, or reading provide a mental break from stress.
- Creative outlets help the brain process emotions and relax.
9. Limit Exposure to Stressors
- Reduce time spent on negative news, social media, and toxic environments.
- Set boundaries at work and in personal relationships.
10. Seek Professional Help When Needed
- If stress becomes overwhelming, therapy, counseling, or stress management programs can be helpful.
- Practices like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) teach effective coping mechanisms.
Conclusion
Stress is a natural part of life, but when left unmanaged, it can negatively impact both physical and mental health. By incorporating healthy habits like exercise, proper sleep, mindfulness, and social connections, you can significantly reduce stress levels and improve your overall well-being.
Instead of trying to eliminate stress completely, focus on managing it effectively so that it does not control your life. Start with small changes today, and over time, these practices will lead to a healthier, more balanced, and stress-free life.